When grappling with severe depression or other challenging mental health conditions, individuals and their healthcare providers often explore a range of treatment options. For those who haven’t found sufficient relief from traditional therapies like medication and psychotherapy, advanced brain stimulation techniques may be considered. Among the most prominent are Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT). While both aim to alleviate symptoms by influencing brain activity, they differ significantly in their approach, invasiveness, side effects, and overall patient experience. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making an informed decision about which therapy might be the most suitable path toward mental wellness.
Understanding the Basics: How Do They Work?
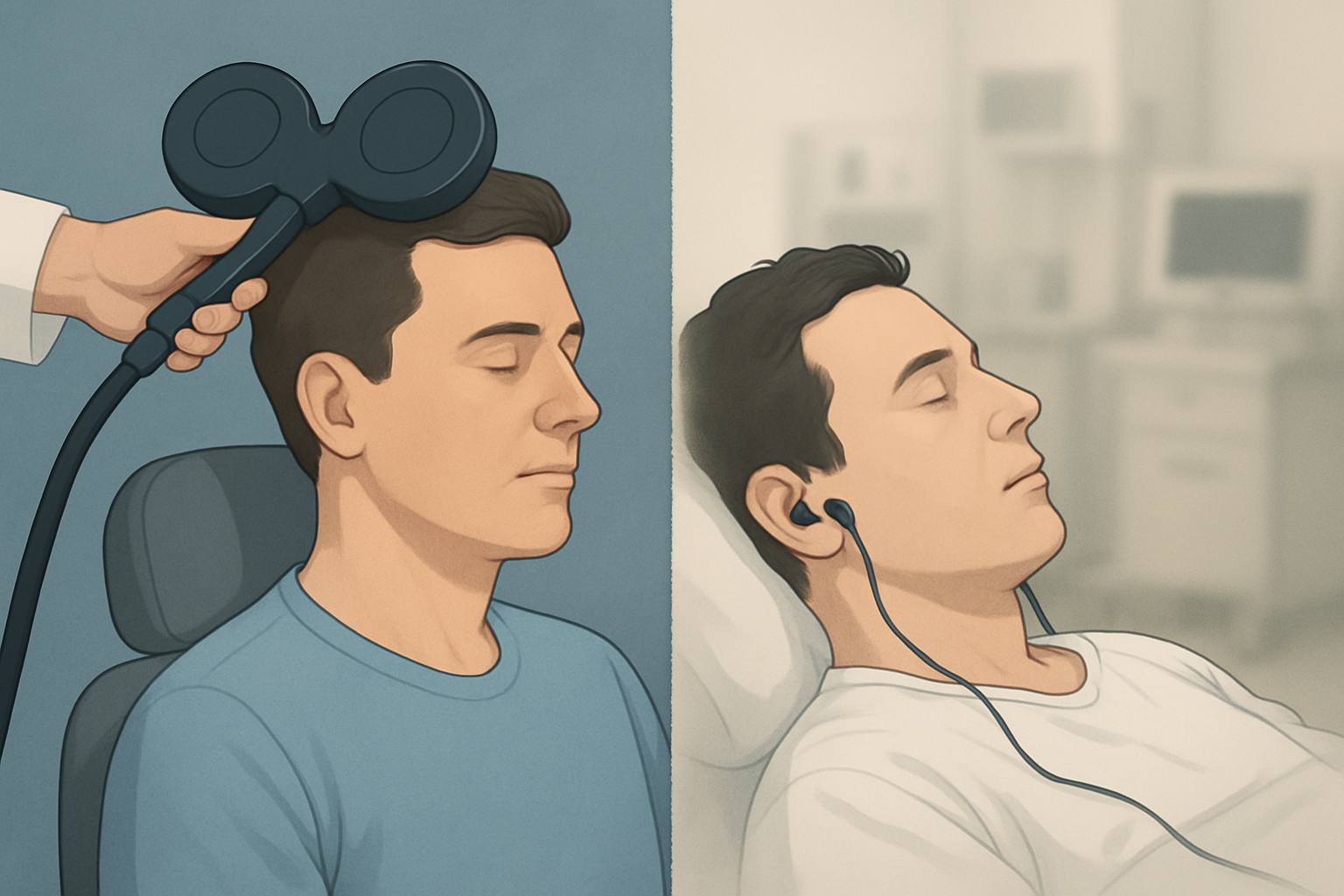
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
TMS is a non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. During a TMS session, an electromagnetic coil is placed on the scalp, typically over the prefrontal cortex—an area of the brain associated with mood regulation. Short, powerful magnetic pulses are delivered through the coil, painlessly passing through the skull and inducing electrical currents in the targeted brain cells. This stimulation is thought to modulate brain activity, helping to restore normal function in areas that are underactive in conditions like depression.
TMS is an outpatient procedure, meaning patients can return to their daily activities immediately after each session. A typical course involves daily treatments, five days a week, for several weeks.
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
ECT, on the other hand, is a more invasive procedure that involves inducing a brief, controlled seizure in the brain. This is done under general anesthesia, with muscle relaxants administered to prevent physical convulsions. Electrodes are placed on the patient’s head, and a carefully controlled electrical current is passed through the brain. While the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, the induced seizure is believed to cause significant neurochemical changes in the brain that can rapidly alleviate severe symptoms of depression, bipolar disorder, and other mental illnesses.
ECT is typically administered in a hospital setting, often three times a week for several weeks, followed by maintenance treatments if necessary.
Key Differences: A Comparative Analysis
The fundamental differences between TMS and ECT extend beyond their mechanisms of action to encompass various aspects of the treatment experience:
Invasiveness and Anesthesia
- TMS: Non-invasive. No surgery, no anesthesia, and no recovery time needed after sessions. Patients are awake and alert during the procedure.
- ECT: Invasive. Requires general anesthesia and muscle relaxants for each treatment. Patients need recovery time in a post-anesthesia care unit.
Side Effects
- TMS: Generally well-tolerated with mild side effects. The most common are mild scalp discomfort or headache at the treatment site, which usually subside after the first few sessions. Seizures are a rare but potential risk (less than 0.1% of patients).
- ECT: Can have more significant side effects due to the induced seizure and anesthesia. Common side effects include temporary memory loss (especially for events around the time of treatment), confusion, headache, muscle aches, and nausea. While memory issues are usually temporary, some patients report persistent memory gaps.
Efficacy and Speed of Response
- TMS: Highly effective for treatment-resistant depression, with remission rates ranging from 30-60% in various studies. The full effects typically become apparent after several weeks of treatment.
- ECT: Often considered the most effective treatment for severe, life-threatening depression, with response rates as high as 70-90%. Its effects can be more rapid, making it a crucial option in acute psychiatric emergencies.
Treatment Setting and Duration
- TMS: Outpatient procedure. Sessions last approximately 20-40 minutes, with a typical course lasting 4-6 weeks.
- ECT: Typically performed in a hospital or specialized clinic. Each treatment session is brief (a few minutes of actual electrical stimulation), but the overall process, including anesthesia and recovery, can take several hours. A course usually involves 6-12 treatments over 2-4 weeks.
Patient Preference and Acceptability
Due to its non-invasive nature and fewer side effects, TMS is often preferred by patients who are apprehensive about ECT or have not responded to medication. The ability to drive and resume daily activities immediately after TMS sessions also contributes to its higher acceptability.
Who is a Candidate for Each Therapy?
TMS Therapy is often considered for:
- Individuals with major depressive disorder who have not responded to antidepressant medications or psychotherapy.
- Patients seeking a non-invasive treatment option with fewer systemic side effects.
- Those who prefer an outpatient treatment that does not require anesthesia.
ECT is typically reserved for:
- Individuals with severe major depression, especially when accompanied by psychosis, severe suicidality, or catatonia.
- Patients with severe bipolar disorder or other psychiatric conditions that have not responded to other treatments.
- Situations where a rapid and definitive response is medically necessary.
Making an Informed Decision
The choice between TMS and ECT is a complex one that should always be made in close consultation with a qualified mental health professional. Your doctor will consider various factors, including the severity of your condition, your medical history, previous treatment responses, potential side effects, and personal preferences. Both therapies represent significant advancements in the treatment of mental illness, offering hope and relief to individuals who may have felt that all other options were exhausted.
At Access Health Services, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive and personalized mental health care. We offer advanced treatments like NeuroStar TMS Therapy as part of our commitment to helping you find the most effective path to wellness. Our team will work closely with you to assess your needs and determine the most appropriate course of treatment. For a broader understanding of our services, including various testing and assessment options, please visit our services page.
We believe in empowering our patients with choices that enable them to embrace a healthy lifestyle and live life with vitality at every stage.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.